Map Coloring In Graph Theory, Graph Coloring Github Topics Github
Map coloring in graph theory Indeed lately is being sought by consumers around us, maybe one of you personally. People are now accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to see video and image information for inspiration, and according to the title of this article I will discuss about Map Coloring In Graph Theory.
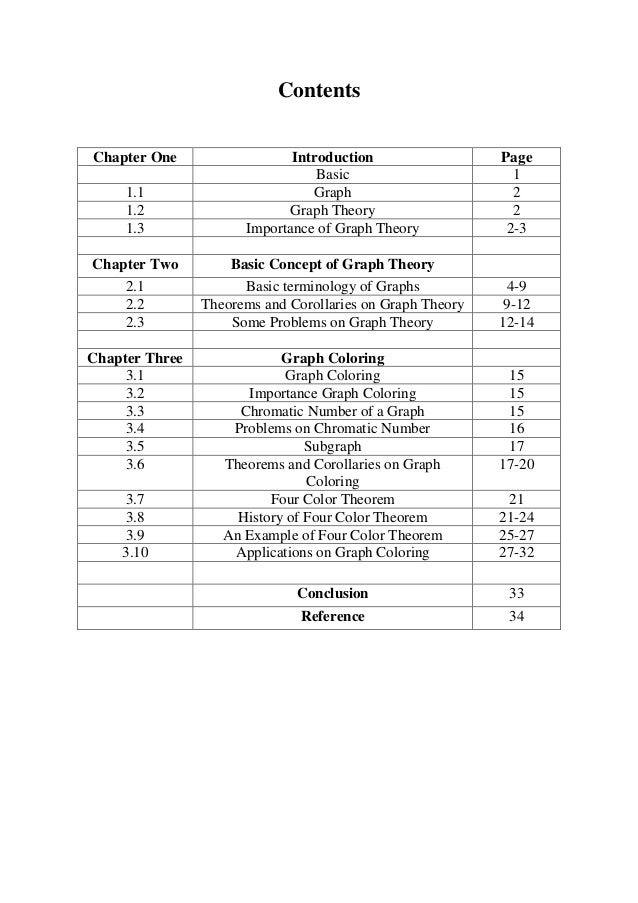
- Coloring
- Map Coloring And Some Of Its Applications
- Math For Seven Year Olds Graph Coloring Chromatic Numbers And Eulerian Paths And Circuits Joel David Hamkins
- Application Of Graph Coloring In Map Coloring And Gsm Mobile Phone Networks Graph Theory Vertex Graph Theory
- 6 3 Graph Coloring Problem Backtracking Youtube
- Four Color Theorem Wikipedia
Find, Read, And Discover Map Coloring In Graph Theory, Such Us:
- Graph Coloring Using Cuda I Team Members
- Application Of Graph Theory In Google Maps Descrete Mathematics Csc 1707 Iium Youtube
- Introduction To Graph Colouring Youtube
- Graph Theory
- Graph Coloring Set 2 Greedy Algorithm Geeksforgeeks
If you are searching for Paint Brush Coloring Page you've reached the right location. We have 104 images about paint brush coloring page adding images, photos, pictures, wallpapers, and much more. In these webpage, we also provide number of graphics available. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, logo, blackandwhite, transparent, etc.
We might also want to use as few different colours as.

Paint brush coloring page. 1007 3137 3157 3203 4115 3261 4156 4118. Graph theory gives us both an easy way to pictorially represent many major mathematical results and insights into the deep theories behind them. A graph coloring is a coloring of graph vertices such that no pair of adjacent vertices share the same color.
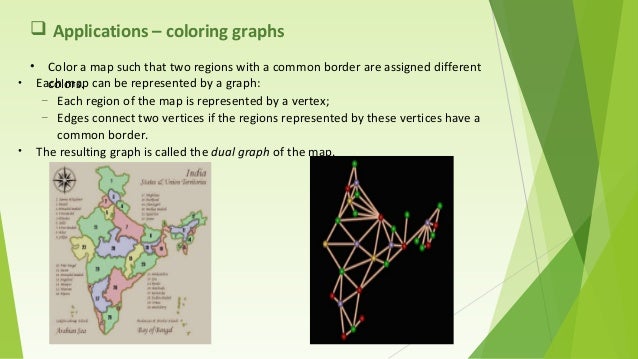
The other graph coloring problems like edge coloring no vertex is incident to two edges of same color and face coloring geographical map coloring can be transformed into vertex coloring. Courses are represented by vertices. As we zoom out individual roads and bridges disappear and instead we see the outline of entire countries.
Graph coloring and scheduling convert problem into a graph coloring problem. Graph coloring is nothing but a simple way of labelling graph components such as vertices edges and regions under some constraints. And the chromatic number of a graph g denoted by capital g is the minimum number of colors needed to color the graph g.
For example the following can be colored minimum. The smallest number of colors needed to color a graph g is called its chromatic number. Coloring regions on the map corresponds to coloring the vertices of the graph.
In a graph no two adjacent vertices adjacent edges or adjacent regions are colored with minimum number of colors. In graph theory graph coloring is a special case of graph labeling. In this course among other intriguing applications we will see how gps systems find shortest routes how engineers design integrated circuits how biologists assemble genomes why a political map.
Weve seen map map colorings and now we will define and see a couple of examples of graph colorings. This number is called the chromatic number and. This is called a vertex coloringsimilarly an edge coloring assigns a color to each.
We have already used graph theory with certain maps. Precise formulation of the theorem. It is an assignment of labels traditionally called colors to elements of a graph subject to certain constraints.
In graph theoretic terms the theorem states that for loopless planar graph the chromatic number of its dual graph is. Coloring a map which is equivalent to a graph sounds like a simple task but in computer science this problem epitomizes a major area of research looking for solutions to problems that are easy to make up but seem to require an intractable amount of time to solve. In its simplest form it is a way of coloring the vertices of a graph such that no two adjacent vertices are of the same color.
Two vertices are connected with an edge if the corresponding courses have a student in common. When colouring a map or any other drawing consisting of distinct regions adjacent countries cannot have the same colour.
More From Paint Brush Coloring Page
- Bee Coloring Template
- Meet The Teacher Coloring Page
- My Little Pony Coloring Fluttershy
- Arianna Name Coloring Pages
- Endangered Animal Coloring Pages
Incoming Search Terms:
- Graph Coloring Or Proof By Crayon Math Programming Endangered Animal Coloring Pages,
- Four Color Theorem Wikipedia Endangered Animal Coloring Pages,
- Coloring Planar Graphs Good Math Bad Math Endangered Animal Coloring Pages,
- Greedy Coloring Wikipedia Endangered Animal Coloring Pages,
- Graph Coloring Wikipedia Endangered Animal Coloring Pages,
- Four Color Theorem Wikipedia Endangered Animal Coloring Pages,